Understanding motion in physics is impossible without discussing the air resistance definition. Whether it is a falling leaf, a moving car, or a flying airplane, air resistance plays a crucial role in determining how objects move through the air. This invisible force constantly interacts with objects around us, shaping speed, direction, and efficiency.
In this detailed guide, we will explore the air resistance definition, its principles, formulas, real-life examples, advantages, disadvantages, and its importance in science and everyday life.
Air Resistance_Definition in Physics
The air resistance definition refers to the force that opposes the motion of an object as it moves through air. It is a type of frictional force caused by collisions between the moving object and air molecules.
In simple terms, air resistance works against motion, slowing objects down as they travel through the air. The faster an object moves, the stronger this force becomes.
Why Understanding the Air Resistance_Definition Matters
Knowing the air resistance definition is important because it helps us understand:
- Why feathers fall slower than stones
- How parachutes work
- Why cars are designed with aerodynamic shapes
- How athletes improve speed and performance
Without air resistance, objects would behave very differently in our environment.
Basic Explanation of the Air Resistance_Definition
At a microscopic level, air consists of tiny molecules. When an object moves through air, it collides with these molecules. These collisions create a force that pushes back against the object’s motion.
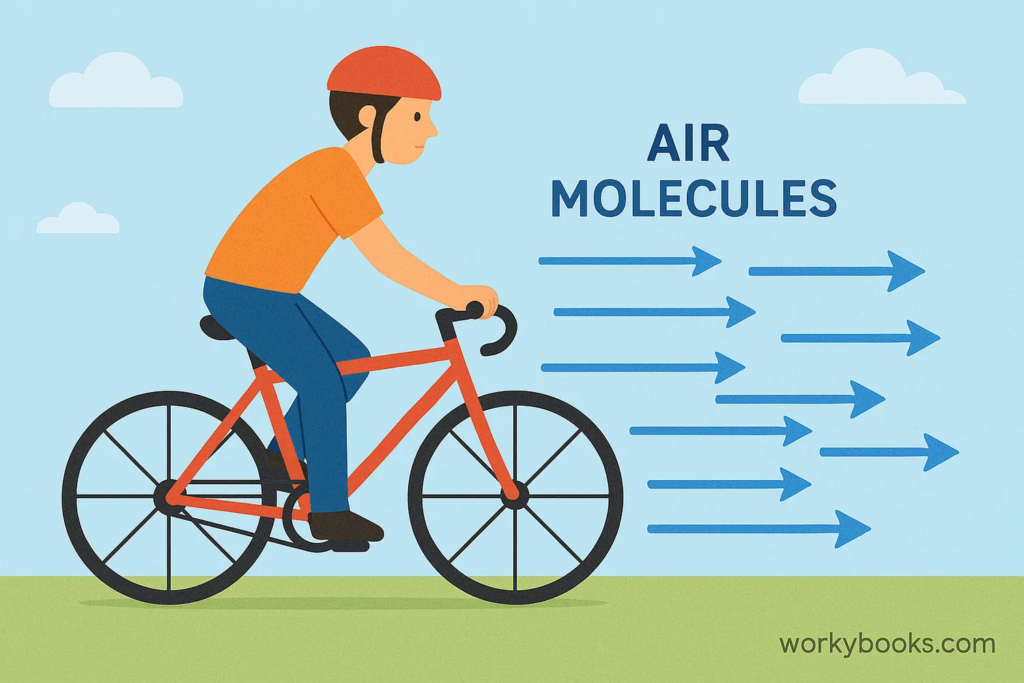
This opposing force is what we call air resistance or drag.
Types of Air Resistance Explained
Understanding the air resistance definition also involves knowing its types.
1. Form Drag
Form drag depends on the shape and size of the object. Objects with larger surface areas face more air resistance.
2. Skin Friction Drag
This type occurs due to friction between air and the surface of the object.
3. Induced Drag
Mostly experienced by flying objects like airplanes, induced drag is created due to changes in air pressure.
Factors That Affect Air_Resistance
The air resistance definition is influenced by several key factors:
Object Speed
As speed increases, air resistance increases rapidly.
Shape of the Object
Streamlined shapes reduce air resistance, while flat or irregular shapes increase it.
Surface Area
Larger surface area means more air molecules collide with the object.
Air Density
Denser air creates more resistance. That’s why objects move differently at high altitudes.
Mathematical Formula Related to Air Resistance_Definition
The standard formula used in physics to calculate air resistance is:
F = ½ × ρ × v² × Cₐ × A
Where:
- F = Air resistance force
- ρ = Air density
- v = Velocity of the object
- Cₐ = Drag coefficient
- A = Cross-sectional area
This formula helps scientists and engineers apply the air resistance definition in real-world calculations.
Air Resistance_Definition with Simple Examples
Let’s simplify the air resistance definition using everyday examples:
- A skydiver falls faster before opening a parachute and slower after opening it.
- A cyclist feels more resistance when riding faster.
- A paper sheet falls slower than a coin when dropped together.
All these examples demonstrate air resistance in action.
Difference Between Air_Resistance and Gravity
Many people confuse gravity with air resistance. Understanding the air resistance definition helps clear this confusion.
| Feature | Gravity | Air Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Direction | Always downward | Opposes motion |
| Cause | Mass attraction | Air molecule collision |
| Effect | Speeds up objects | Slows down objects |
Both forces act together to determine motion.
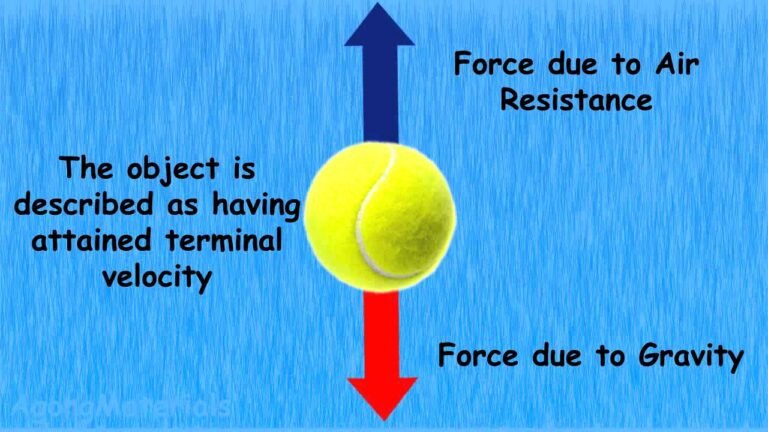
Terminal Velocity and Air Resistance_Definition
Terminal velocity is directly connected to the air resistance definition.
When air resistance equals the force of gravity, an object stops accelerating and moves at a constant speed. This maximum speed is known as terminal velocity.
Skydivers rely on this principle for safety and control.
Air Resistance_Definition in Sports
Sports professionals consider air resistance seriously.
Examples:
- Cyclists wear aerodynamic helmets
- Swimmers reduce drag using streamlined techniques
- Runners adjust posture to minimize resistance
In competitive sports, understanding the air resistance definition can be the difference between winning and losing.
Air Resistance_Definition in Vehicles
Modern vehicles are designed with aerodynamics in mind.
Why It Matters:
- Reduces fuel consumption
- Improves speed
- Enhances stability
Car manufacturers use wind tunnels to test designs based on the air resistance definition.
Air Resistance_Definition in Aviation
Airplanes depend heavily on managing air resistance.
- Wings are shaped to reduce drag
- Jet engines are streamlined
- Landing gear retracts to lower resistance
Without understanding the air resistance definition, aviation would not be possible.
Advantages of Air Resistance
Although often seen as a negative force, air resistance has benefits:
- Allows parachutes to function
- Helps slow down vehicles
- Prevents objects from falling dangerously fast
The air resistance definition shows that this force plays a protective role in many situations.
Disadvantages of Air Resistance
Despite its advantages, air resistance also has drawbacks:
- Reduces speed
- Increases fuel usage
- Limits efficiency
Engineers constantly work to minimize these effects while respecting the air resistance definition.
Air Resistance Definition in Space vs Earth
On Earth, air resistance affects nearly all motion. In space, where there is no air, objects move without resistance.
This explains why astronauts float and why objects keep moving unless acted upon by another force.
Common Misconceptions About Air Resistance Definition
Some common misunderstandings include:
- Air resistance only affects light objects ❌
- Air resistance is constant ❌
- Faster objects experience less resistance ❌
In reality, the air resistance definition proves the opposite.
How Scientists Measure Air Resistance
Scientists measure air resistance using:
- Wind tunnels
- Motion sensors
- Computational fluid dynamics
These tools help apply the air resistance definition accurately in research and engineering.
Air Resistance Definition in Education
The concept is taught in:
- School physics textbooks
- Engineering courses
- Aviation training programs
A strong grasp of the air resistance definition builds a foundation for advanced scientific understanding.
Real-World Applications of Air Resistance Definition
Some real-world uses include:
- Designing sports equipment
- Improving fuel efficiency
- Weather forecasting
- Aerospace engineering
Every application relies on the correct understanding of air resistance.
Future Innovations Based on Air Resistance
As technology advances, researchers aim to:
- Reduce drag using new materials
- Improve transportation efficiency
- Develop eco-friendly designs
The air resistance definition will remain central to innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions About Air Resistance Definition
What is the simplest air resistance definition?
Air resistance is the force that slows down objects moving through air.
Does air resistance depend on weight?
No, it mainly depends on shape, speed, and surface area.
Can air resistance be eliminated?
Only in a vacuum; on Earth, it cannot be completely removed.